TimberTech Aluminum Framing: Costs, Benefits, and Comparison with Fortress Framing
Introduction to TimberTech Aluminum Framing
In the ever-evolving world of construction and decking, TimberTech aluminum framing has emerged as a modern and reliable material choice. As the demand for sustainable and durable building solutions grows, aluminum framing is gaining popularity for its exceptional properties. TimberTech, a leader in innovative decking solutions, offers aluminum framing that stands out in the industry for its durability and aesthetic appeal.
Why is aluminum framing becoming a preferred choice? Unlike traditional wood options, TimberTech aluminum framing offers superior resistance to environmental factors such as weathering and corrosion, making it ideal for long-term applications. Its lightweight nature simplifies installation, reducing labor costs and time, which is a significant advantage in both residential and commercial projects. Additionally, aluminum's recyclability aligns with the growing trend towards eco-friendly building practices.
While TimberTech sets a high standard in aluminum framing, it's essential to consider alternatives like Fortress Framing and other aluminum structural framing options. These comparisons will be explored further in this article to provide a comprehensive understanding of where TimberTech stands in the market. Whether you're a homeowner or a contractor, understanding these options can significantly impact your project's success and sustainability.
What is TimberTech Aluminum Framing?
TimberTech aluminum framing is an advanced construction material designed to offer a robust and sustainable foundation for decking projects. This framing system comprises several key components, including joists, posts, ledgers, and beams, all engineered from high-grade aluminum. Such components are meticulously crafted to ensure strength and durability, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications.
The manufacturing process of TimberTech aluminum components involves precision engineering to create a lightweight yet sturdy framework. Aluminum's inherent properties, such as resistance to rust, corrosion, and insect damage, are enhanced through this process, ensuring that the framing system remains unaffected by environmental challenges. This makes it a superior choice compared to traditional materials like wood, which can succumb to moisture and decay over time.
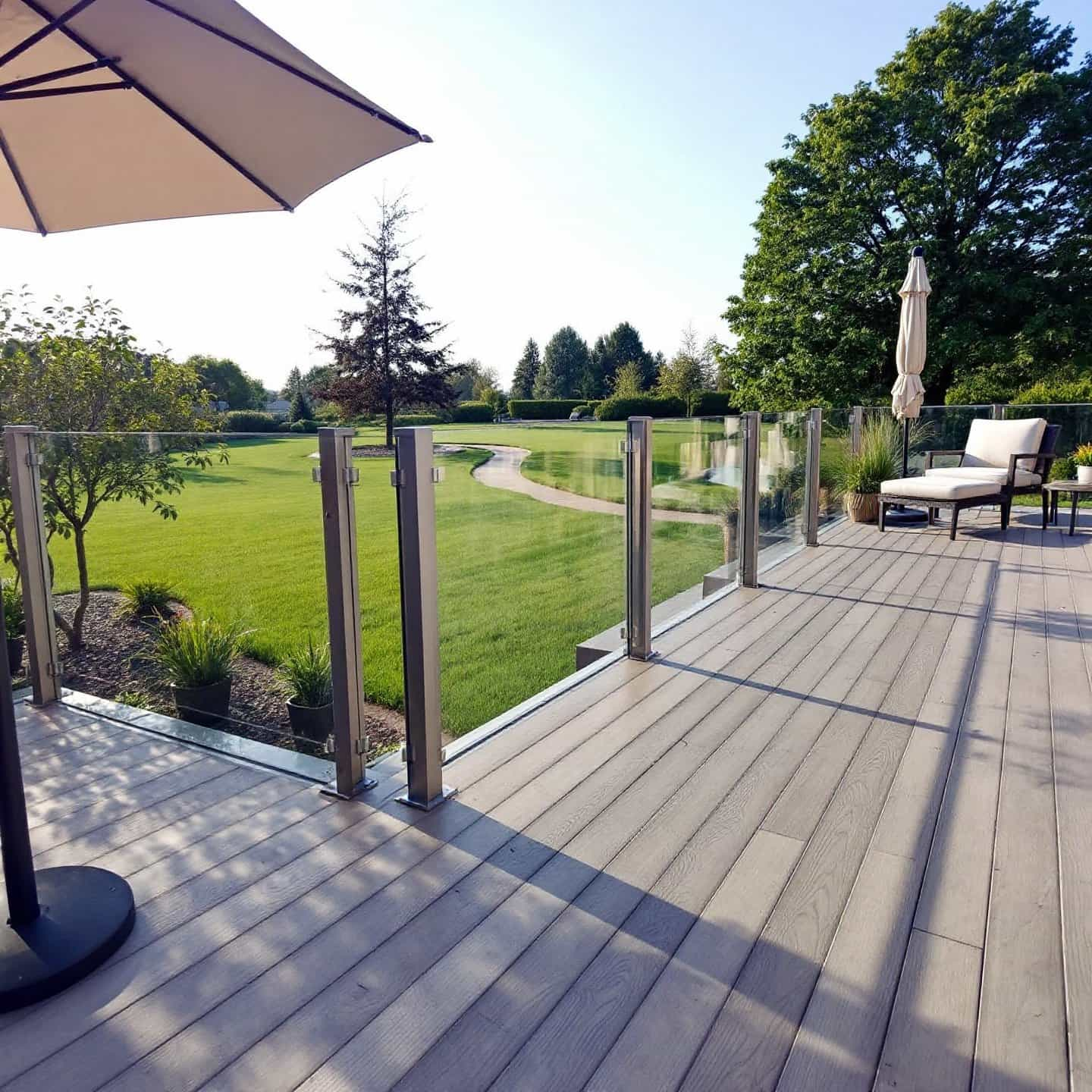
In terms of application, TimberTech aluminum framing is a cornerstone in modern construction, particularly in the realm of aluminum decking systems. Its versatility allows for seamless integration with various decking and railing products, providing a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing outdoor space. The system's design supports expansive spans and cantilevered overhangs, offering greater flexibility in deck layout and design.
Imagine transforming your outdoor area with a decking system that not only looks great but also stands the test of time. With TimberTech's innovative aluminum framing, you’ll notice a significant enhancement in the performance and longevity of your deck, ensuring it remains a beautiful and functional space for years to come.
Key Features and Benefits of TimberTech Aluminum Framing
When considering materials for your next decking project, TimberTech aluminum framing offers a compelling array of benefits that make it a standout choice. Imagine a framing system that not only supports your deck but also enhances its longevity and sustainability. This is precisely what TimberTech delivers, combining durability with eco-friendly attributes.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
One of the most significant advantages of TimberTech's aluminum framing is its outstanding durability. Engineered to withstand the harshest environmental conditions, this framing system is highly resistant to moisture damage, such as rust and corrosion. Unlike traditional wood, which can warp or rot over time, TimberTech's durable aluminum framing maintains its structural integrity, ensuring your deck remains stable and secure for years.
Additionally, TimberTech aluminum framing boasts a Class A Flame Spread Rating, making it an excellent choice for fire-prone areas. This rating signifies that the material is unlikely to contribute to the spread of flames, offering peace of mind and added safety for homeowners.
Low Maintenance and Environmental Benefits
Another appealing feature of TimberTech aluminum framing is its low maintenance requirements. Unlike wood, which demands regular sealing and treatment to prevent decay and insect damage, aluminum framing is virtually maintenance-free. This translates into significant time and cost savings over the lifespan of your deck.
Moreover, TimberTech aluminum framing is a champion of sustainability. Made from recyclable deck materials, it supports eco-friendly building practices by minimizing waste and promoting recyclability at the end of its useful life. This aligns perfectly with the growing trend towards sustainable construction, making it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious builders and homeowners alike.
In summary, TimberTech aluminum framing offers a robust, low-maintenance, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional materials. Its exceptional durability and recyclability make it an ideal choice for those looking to invest in a long-lasting and sustainable decking solution. As we explore further, you'll see how these features stack up against other framing options, guiding you toward the best choice for your project.
Advantages Over Traditional Wood Decking
When considering the optimal materials for decking, a comparison between TimberTech aluminum framing and traditional wood framing reveals significant advantages. Let's explore how these two materials stack up against each other in terms of durability, installation time, and maintenance costs.
Durability
- TimberTech Aluminum Framing: Known for its exceptional strength, aluminum framing is resistant to warping, rotting, and insect damage. It maintains structural integrity even in harsh weather conditions, offering a lifespan that can exceed 40 years.
- Traditional Wood Framing: While wood is initially cheaper, it is prone to warping, rotting, and insect infestation. Its durability significantly decreases without regular maintenance, typically lasting 10-15 years.
Installation Time
- TimberTech Aluminum Framing: Lightweight and easy to handle, aluminum framing reduces installation time. Its precision-engineered components fit together seamlessly, minimizing labor costs and complexity.
- Traditional Wood Framing: Heavier and more labor-intensive, wood requires more time and effort to install. Adjustments and modifications are often necessary, which can extend the installation timeline.
Maintenance Costs
- TimberTech Aluminum Framing: Offers a low maintenance solution, requiring little more than occasional cleaning. Its resistance to environmental factors means no need for regular sealing or treatments.
- Traditional Wood Framing: Demands ongoing maintenance, including staining, sealing, and treating to prevent decay and damage. These recurrent tasks lead to higher long-term costs.
In summary, when comparing aluminum vs wood decking , TimberTech aluminum framing stands out for its durability, reduced installation time, and low maintenance requirements. These advantages make it a compelling choice for homeowners seeking a long-lasting and cost-effective decking solution. As we move forward, we'll delve into the cost efficiency of TimberTech aluminum framing, highlighting how it offers long-term savings compared to traditional materials.
Cost Efficiency of TimberTech Aluminum Framing
When planning a decking project, understanding the cost implications of different materials is crucial. TimberTech aluminum framing stands out as a cost-efficient decking solution, offering significant long-term savings that can outweigh its initial investment.
While the upfront cost of TimberTech aluminum framing may be higher compared to traditional wood options, the real savings become apparent over time. One of the key factors contributing to this cost efficiency is its low maintenance needs. Unlike wood, which requires regular sealing, staining, and repairs due to weathering and insect damage, aluminum framing remains virtually maintenance-free. This means homeowners can avoid the recurring expenses associated with maintaining a wood deck, such as annual treatments and repairs, which can add up significantly over the years.
Moreover, TimberTech aluminum framing's durability ensures a longer lifespan, reducing the likelihood of costly replacements. With an expected lifespan exceeding 40 years, it offers peace of mind and sustained value. This longevity, coupled with minimal upkeep, translates into long-term decking savings, making it an attractive option for those looking to maximize their investment.
Additionally, the recyclability of aluminum contributes to its cost efficiency from an environmental perspective. As sustainability becomes a priority for many homeowners, choosing recyclable deck materials like TimberTech aligns with eco-friendly practices, potentially increasing property value and appeal.
In conclusion, investing in TimberTech aluminum framing not only promises a robust and aesthetically pleasing deck but also ensures cost-efficient decking through reduced maintenance and extended lifespan. As we continue, we'll explore a detailed cost comparison between TimberTech and other framing options, providing further insights into making the best financial decision for your decking project.
TimberTech vs Fortress Framing: Cost Comparison
When selecting a framing system for your decking project, understanding the cost dynamics between different options is crucial. Let's delve into a detailed comparison between TimberTech aluminum framing and Fortress steel framing to help you make an informed decision.
| Aspect |
TimberTech Aluminum Framing |
Fortress Steel Framing |
| Material Costs |
$15 to $20 per square foot (source) |
Higher initial cost due to steel's premium pricing |
| Installation Costs |
Lower due to lightweight and ease of handling |
Potentially higher due to complexity and need for specialized tools (source) |
| Long-Term Maintenance |
Minimal; aluminum resists rust and corrosion |
Low; steel is galvanized to prevent rust but may require occasional checks |
| Durability and Lifespan |
Exceeds 40 years, resistant to environmental damage |
Comparable lifespan with added fire resistance benefits |
| Environmental Impact |
Recyclable, supporting sustainable building practices |
Highly recyclable, contributing to environmental sustainability |
From the table, it's clear that both TimberTech and Fortress offer robust solutions, but they cater to slightly different needs. TimberTech aluminum framing is cost-effective in terms of installation and long-term maintenance, making it a great choice for those prioritizing ease of use and sustainability. Its lightweight nature reduces labor costs and simplifies the installation process, which can be a significant advantage if you're working within tight project timelines or budgets.
On the other hand, Fortress steel framing, while potentially more expensive initially, provides added benefits such as fire resistance and greater structural strength, which might be crucial in certain environments or specific project requirements. However, the complexity of installation can increase labor costs, so it's essential to factor this into your budget.
In conclusion, the choice between TimberTech and Fortress framing should be guided by your specific project needs, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance preferences. As you plan your decking project, consider these factors carefully to ensure the best value and performance for your investment. Next, we'll explore the detailed costs involved in a typical TimberTech aluminum framing project, providing further clarity on budgeting for your decking needs.
Understanding TimberTech Aluminum Framing Costs
When embarking on a decking project with TimberTech aluminum framing, it's crucial to understand the various costs involved to effectively plan your budget. The expenses can be broken down into several key categories: materials, labor, and additional costs that may arise based on specific project requirements.
Material Costs
The cost of materials is a significant component of your overall budget. TimberTech aluminum framing typically ranges from $15 to $20 per square foot. This cost includes the essential components like joists, beams, and posts that form the deck's substructure. Compared to traditional wood, aluminum's higher initial cost is offset by its longevity and minimal maintenance needs, offering long-term savings.
Labor Costs
Labor is another substantial part of deck project expenses. The lightweight nature of aluminum framing reduces installation time and complexity, potentially lowering labor costs compared to heavier materials like steel or wood. However, hiring a skilled contractor familiar with aluminum systems is crucial to ensure proper installation and maximize the framing's benefits.
Additional Costs
Beyond materials and labor, several additional factors can influence the overall cost of your TimberTech project. The size and complexity of the deck design play a pivotal role; larger or more intricate designs naturally incur higher costs. Location is another factor—areas with higher labor rates or stricter building codes may see increased expenses. Furthermore, site preparation, such as clearing or leveling the land, and obtaining necessary permits can add to the cost.
In conclusion, while the initial investment in TimberTech aluminum framing may be higher than some alternatives, its durability, low maintenance, and environmental benefits offer substantial value over time. Understanding these costs and planning accordingly will help ensure a successful and budget-friendly decking project.
Integration with Aluminum Structural Framing
When considering large-scale construction projects, integrating TimberTech aluminum framing with other aluminum structural systems can offer significant advantages. This integration not only enhances the overall strength of the structure but also provides greater design flexibility, making it an attractive option for architects and builders seeking innovative solutions.
Benefits of Hybrid Framing Systems
Hybrid framing systems, which combine TimberTech aluminum with other structural aluminum components, offer a unique blend of benefits. Imagine a framework that leverages the lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties of aluminum while incorporating the robust support of additional structural elements. This approach optimizes the structural integrity of the building, ensuring it can withstand various environmental stresses.
One of the standout benefits of hybrid systems is their adaptability. By using a combination of materials, builders can tailor the structure to meet specific design and performance requirements. For instance, in areas prone to seismic activity, the flexibility of aluminum can be paired with more rigid materials to enhance earthquake resistance. This adaptability makes hybrid framing systems ideal for a wide range of applications, from residential buildings to large industrial complexes.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Another significant advantage of integrating TimberTech aluminum framing with other systems is the enhanced design flexibility it offers. Aluminum's malleability allows for creative architectural designs that might be challenging with traditional materials. This flexibility enables architects to achieve unique aesthetic goals without compromising on structural performance.
Moreover, aluminum's sleek and modern appearance can be seamlessly integrated with other materials to create visually appealing structures. Whether you're aiming for a contemporary look or a more traditional design, hybrid systems provide the versatility needed to bring your vision to life.
In conclusion, integrating TimberTech aluminum framing with other aluminum structural systems in larger projects not only optimizes strength and design flexibility but also enhances the overall aesthetic appeal. This approach allows builders and architects to maximize the benefits of aluminum, creating structures that are both durable and visually striking. As you plan your next construction project, consider the advantages of hybrid framing systems to achieve the best of both worlds in terms of performance and design.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of TimberTech aluminum framing, it's clear that this innovative material offers a host of benefits that make it a standout choice for decking solutions. Its durability, with resistance to rust, corrosion, and environmental wear, ensures a long-lasting structure that maintains its integrity and aesthetic appeal over time. This makes TimberTech an ideal investment for those seeking a robust and visually pleasing deck.
Cost-effectiveness is another key advantage. While the initial investment may be higher than traditional wood, the long-term savings from low maintenance and extended lifespan make TimberTech aluminum framing a financially savvy choice. The material's recyclability further enhances its appeal, aligning with sustainable building practices and potentially increasing property value.
For those considering their next project, TimberTech provides a comprehensive solution that meets both practical and aesthetic needs. Whether you're enhancing a residential space or embarking on a commercial venture, the benefits of TimberTech aluminum framing are undeniable. We encourage you to explore the possibilities and request a TimberTech project quote to understand specific costs tailored to your needs.
Additionally, for those interested in a broader perspective on aluminum framing options, Suqian Sunmay Aluminium stands out as a leader in the industry. Their expertise in crafting high-quality aluminum profiles offers a wealth of opportunities for various applications, ensuring that your project benefits from the best materials available. To learn more about their offerings and capabilities, visit their official website .
In conclusion, TimberTech aluminum framing represents a modern, efficient, and sustainable choice for decking projects. By integrating advanced materials and design flexibility, it ensures that your investment delivers both immediate and long-term value. Consider TimberTech for your next decking project and experience the difference in quality and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is aluminum framing good?
Aluminum framing is highly regarded for its lightweight nature and structural integrity, making it a cost-effective and durable option for construction.
2. What is TimberTech decking made of?
TimberTech decking incorporates wood fibers and recycled plastics, offering a sustainable and durable decking solution.
3. How does TimberTech aluminum framing compare to wood?
TimberTech aluminum framing is more durable and requires less maintenance than wood, offering long-term savings and resistance to environmental factors.
4. What are the benefits of hybrid framing systems?
Hybrid framing systems combine materials like aluminum for enhanced strength and flexibility, optimizing structural integrity and design possibilities.
5. How can I integrate TimberTech aluminum framing into larger projects?
TimberTech aluminum framing can be integrated with other structural systems, offering design flexibility and enhanced durability for larger construction projects.